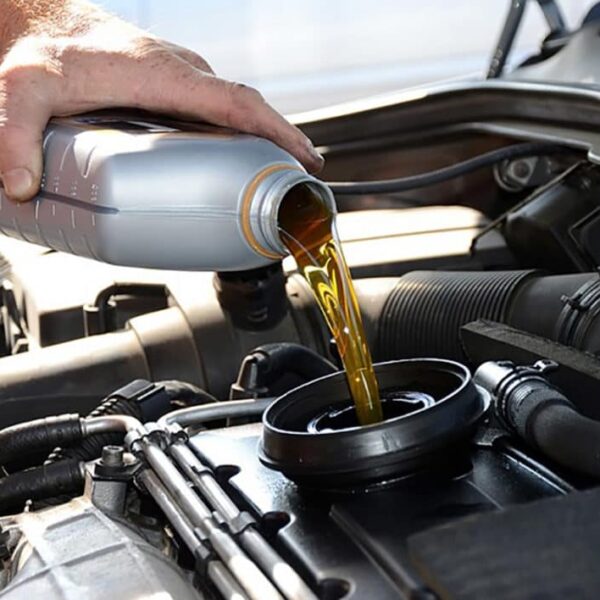
2-stroke and 4-stroke engine oils are designed to meet the unique needs of their specific engine types. In 2-stroke engines, the oil is mixed with fuel and burns during combustion to lubricate moving parts. In contrast, 4-stroke engines use oil that circulates separately through the engine, providing continuous lubrication without being burned. This fundamental difference affects how each oil performs and where it should be used—making it important to choose the right type for your engine.
Choosing between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine oils can sometimes feel tricky, especially when dealing with different types of engines. Whether you’re maintaining a chainsaw or keeping your car in top shape, it’s important to understand how engines work and why they need specific oils.
The two main types of small engines are 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. Both types use similar parts, like pistons and spark plugs, but they operate differently. The oil you use in these engines isn’t the same either—each type has its own specific needs.
In this article, we’ll break down how 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines work, and most importantly, how their oils differ. This knowledge will help you make the right choice when maintaining your engines, ensuring they last longer and run smoothly.
Why Understanding Engine Oil is Important
If you’ve ever wondered why your lawnmower’s oil isn’t the same as your car’s, there’s a good reason. Engine oil does much more than just lubricate—it protects, cleans, and helps the engine cool down. Using the wrong oil can damage your engine, reduce its efficiency, and even increase harmful emissions.
Fun Fact: Did you know that using the correct oil can reduce your engine’s wear and tear by up to 30%? That’s why knowing the difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke oil is so important.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand:
- What 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines are
- How they differ in operation
- Why each engine needs a different type of oil
- How to choose the right oil for your specific engine
Now, let’s dive into the details!
What Are 2-Stroke Engines?
A 2-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine designed to complete a power cycle in just two strokes (one upstroke and one downstroke) of the piston. This design allows for faster power generation compared to a 4-stroke engine, making it more efficient for certain applications. In simple terms, a 2-stroke engine compresses, ignites, and exhausts the fuel in just one cycle of the piston moving up and down, while the more common 4-stroke engine takes twice as long.
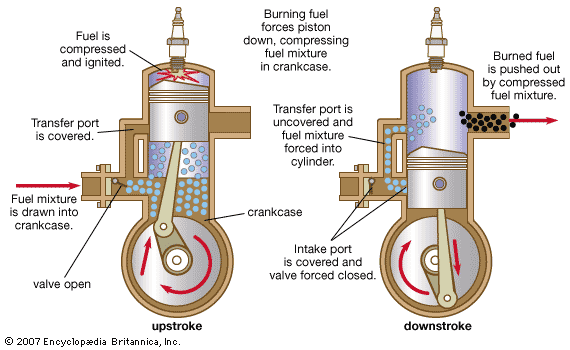
Image source britannica.com: Example of a 2-stroke engine cycle, illustrating its compact design.
How Does a 2-Stroke Engine Work?
Unlike 4-stroke engines that have separate stages for intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, a 2-stroke engine combines these processes. Here’s a breakdown:
- Intake & Compression: As the piston moves up, it compresses the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder. At the same time, a new charge of fuel and air is drawn into the crankcase.
- Combustion & Exhaust: When the piston reaches the top of the cylinder, the spark plug ignites the compressed fuel-air mixture, creating an explosion that forces the piston back down. This movement opens the exhaust ports to expel the burnt gases, while also pushing the fresh fuel mixture from the crankcase into the cylinder for the next cycle.
This simplicity is why 2-stroke engines produce power every time the piston moves, making them lighter and more powerful for their size compared to 4-stroke engines.
Key Components of a 2-Stroke Engine
- Piston: Moves up and down inside the cylinder.
- Crankcase: A part of the engine that helps with the gas exchange, acting like a pump.
- Transfer Ports: These allow the fuel mixture to move from the crankcase into the cylinder.
- Spark Plug: Ignites the fuel-air mixture to create the explosion that drives the piston.
Applications of 2-Stroke Engines
You won’t find a 2-stroke engine under the hood of your car or truck, but they are perfect for small machines that need lightweight, high-power engines. Some common places you’ll encounter a 2-stroke engine include:
- Lawnmowers
- Chainsaws
- Dirt bikes
- Outboard boat motors
- Go-karts
These engines are favored because of their compact size and power-to-weight ratio. Imagine trying to use a 4-stroke engine in a chainsaw; it would be too heavy and bulky to manage easily. A 2-stroke engine allows small machines to remain portable, which is essential in these applications.
Advantages of 2-Stroke Engines
2-stroke engines come with several key advantages that make them popular in certain sectors:
- Lightweight and Compact: Their design is simpler, with fewer parts (like valves), making them lighter and easier to maintain.
- High Power Output: Since the engine fires every time the piston completes a cycle, it delivers more power relative to its size.
- Cost-Effective: Their design is simple, so they cost less to manufacture and repair.
Drawbacks of 2-Stroke Engines
Even though they’re efficient, 2-stroke engines have some significant downsides:
- Environmental Impact: Because the fuel and oil mix together, 2-stroke engines tend to emit a lot of pollution. Burning oil creates smoke and unburned fuel emissions.
- Less Fuel-Efficient: These engines burn through fuel more quickly than 4-stroke engines.
- Noisy & Vibrates More: They can be much louder and produce more vibrations, which isn’t ideal for long-term use in larger vehicles.
Expert tip: If you’re using a 2-stroke engine for yard work or small machinery, it’s essential to use synthetic 2-stroke oil. Not only does this help reduce pollution, but it also keeps your engine running cleaner and smoother. One of the most reliable brands is Valvoline’s SynPower 2T, designed specifically to minimize smoke and protect your engine even under harsh conditions.
Real-Life Example of 2-Stroke Use
I’ve worked on plenty of 2-stroke engines during my career as a mechanic, particularly in smaller machines like chainsaws and go-karts. One thing I’ve always appreciated about 2-stroke engines is their simplicity—if something goes wrong, you can usually fix it without needing tons of expensive parts or tools. In fact, I remember fixing a 2-stroke outboard motor during a fishing trip. The engine stalled, and after a quick inspection, I found that the spark plug was fouled from the oil-fuel mix. A clean spark plug was all it took to get us back on the water, ready for more fishing.
Final Thoughts on 2-Stroke Engines
While 2-stroke engines are becoming less common due to their environmental impact, they remain a practical choice for small machines that need high power output without the bulk. The balance between portability, power, and cost makes them essential for tools and vehicles like dirt bikes, chainsaws, and lawnmowers. However, the trend is shifting towards more eco-friendly options, with manufacturers developing better oils and more efficient designs.
What Are 4-Stroke Engines?
A 4-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine that works through four separate steps: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. These four strokes make up one complete power cycle, hence the name “4-stroke.”
Unlike a 2-stroke engine, which completes the cycle in just two piston movements (up and down), a 4-stroke engine takes four. This design makes the 4-stroke engine more efficient, cleaner, and longer-lasting compared to its 2-stroke counterpart.
How a 4-Stroke Engine Works
Let’s break down each of these four strokes to make it easy to understand:
- Intake: The piston moves down, and a mixture of air and fuel is drawn into the combustion chamber.
- Compression: The piston moves back up, compressing the air-fuel mixture to prepare it for ignition.
- Power (Combustion): A spark plug ignites the compressed fuel, and the resulting explosion pushes the piston back down. This is where the engine gets its power.
- Exhaust: Finally, the piston moves up again, expelling the burnt gases out of the engine through the exhaust valve.
This process repeats over and over, and that’s what powers vehicles like cars, motorcycles, and even some trucks. Each stroke is important because separating these steps makes the engine more controlled and efficient.
Why Are 4-Stroke Engines So Popular?
One of the main reasons 4-stroke engines are widely used is their efficiency. Because each stroke is done separately, the engine burns fuel more thoroughly, which means fewer pollutants are emitted.
Here are a few reasons why 4-stroke engines are commonly found in cars, motorcycles, and lawnmowers:
- Better fuel efficiency: Since 4-stroke engines don’t mix oil and fuel, they use less fuel over time compared to 2-strokes.
- Less pollution: Separating fuel and oil results in cleaner emissions, which is better for the environment.
- Quieter operation: 4-stroke engines tend to be quieter and smoother than 2-strokes because they don’t fire with every crankshaft revolution.
- Durability: These engines are built to last longer due to their design, requiring less frequent maintenance and oil changes.
An Expert’s Advice on 4-Stroke Engines
From my years as a mechanic, I’ve seen firsthand how 4-stroke engines dominate the market for everyday vehicles. They are easier to maintain, and their components wear down slower. However, here’s a tip that most people overlook:
Regular oil changes are critical. The oil in a 4-stroke engine doesn’t burn off like in a 2-stroke engine, but it still gets dirty and loses its effectiveness over time. Stick to a regular maintenance schedule, and always use the oil recommended by the manufacturer. Doing this will extend the engine’s life significantly.
Pro Tip: Never ignore a rattling sound coming from your 4-stroke engine. It’s often a sign that something’s wrong with the timing chain or valves—and trust me, you don’t want those parts failing!
Applications of 4-Stroke Engines
Here are some common machines that use 4-stroke engines:
- Passenger cars
- Motorcycles
- Generators
- Marine engines
- Lawnmowers
These engines are particularly popular in modern vehicles because they offer a great balance between power, efficiency, and reliability. If you’ve ever wondered why your car runs smoothly for long distances, you can thank the 4-stroke engine design.
In conclusion, 4-stroke engines are everywhere, and for good reason. They offer efficiency, power, and cleaner emissions, making them ideal for vehicles we rely on daily. Just remember to take care of them, and they’ll last a long time!
What Is 2-Stroke Engine Oil?
Two-stroke engine oil, often referred to as 2T oil, plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of small engines, such as those found in lawnmowers, chainsaws, and motorcycles. Unlike 4-stroke engines, where oil and fuel are kept separate, 2-stroke engines require the oil to mix with fuel. This blend lubricates the engine as it runs, keeping all the moving parts from wearing down prematurely.
The Basics of 2-Stroke Oil Composition
2-stroke engine oil consists of a base oil and a range of additives that improve performance and protect the engine. These additives reduce friction, prevent rust, and keep the engine cleaner by removing impurities. The base oil can come from different sources, including:
- Castor oil
- Petroleum-based oils
- Semi-synthetic blends
- Fully synthetic oils
Modern engines typically use synthetic oil, which is designed to burn more cleanly. This minimizes emissions and helps reduce carbon buildup on critical parts like the spark plug.
How 2-Stroke Engine Oil Works
In a 2-stroke engine, the crankcase isn’t used for oil storage as it is in 4-stroke engines. Instead, it’s part of the induction system. When the fuel-oil mixture enters the engine, it lubricates the cylinder walls, piston, and crankshaft. This process happens very quickly, as every revolution of the crankshaft leads to combustion—giving 2-stroke engines their signature high power output.
Important Note: A common fuel-to-oil ratio is 50:1, meaning for every 50 parts of fuel, there is 1 part of oil. However, this ratio can vary depending on the manufacturer and specific engine requirements. Always check your engine’s manual to ensure the correct mixture.
Benefits of Using Synthetic 2-Stroke Oils
Synthetic 2-stroke oils, like Valvoline SynPower 2T, are especially beneficial for reducing smoke and pollution. They also offer superior protection, even under extreme operating conditions, such as high temperatures or heavy loads. The components used in synthetic oils are more refined, ensuring fewer deposits are left inside the engine, which means less maintenance and longer engine life.
- Cleaner burns: Reduces smoke and lowers environmental impact.
- Less ash content: Prevents buildup on the spark plug and exhaust system.
- Improved fuel efficiency: Synthetic oils often help engines run more efficiently, providing better fuel economy.
Additives in 2-Stroke Oil
To further enhance performance, manufacturers add specific chemicals to 2-stroke oils. These include:
- Detergents: Help keep the engine clean by preventing the buildup of carbon and other deposits.
- Anti-wear agents: Protect metal surfaces from friction and wear, prolonging engine life.
- Biodegradability components: Make the oil less harmful to the environment when it’s burned.
- Fuel stabilizers: Keep the oil-fuel mix fresh and prevent it from breaking down when stored.
By choosing a high-quality oil, like Valvoline Super Outboard 2T, you can be sure that your engine will run efficiently and reliably, with fewer emissions and less need for repairs.
Why Proper 2-Stroke Oil Matters
Using the wrong oil in a 2-stroke engine can lead to engine failure, increased wear, and even permanent damage. Because 2-stroke engines rely so heavily on the oil-fuel mixture for both lubrication and power, making sure you use the right oil is vital.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what happens when you choose the correct oil:
- Lubrication: Keeps all moving parts running smoothly, reducing wear and friction.
- Combustion: Helps the fuel burn more efficiently, leading to better power output and fewer emissions.
- Cooling: As the oil moves through the engine, it absorbs heat and helps prevent overheating.
Final Thoughts on 2-Stroke Engine Oil
In summary, 2-stroke engine oil is more than just a lubricant—it’s a critical part of how these engines operate. By using high-quality oil, you’ll protect your engine, reduce maintenance costs, and even help the environment by lowering emissions. For the best performance, especially in modern engines, always opt for synthetic 2T oils with low ash content, like Valvoline’s offerings.
What Is 4-Stroke Engine Oil?
Four-stroke engine oil is a specific type of oil designed to lubricate and protect the internal components of a four-stroke engine. Unlike 2-stroke engines, where the oil is mixed directly with the fuel, 4-stroke engines have a separate oil system. This means that the oil circulates through the engine to lubricate various moving parts, but it doesn’t burn with the fuel.
In simpler terms, imagine your engine as a machine with many parts that move constantly—like pistons, valves, and crankshafts. These parts generate a lot of heat and friction. Without oil, they’d grind against each other and quickly wear out. Four-stroke engine oil keeps everything running smoothly by creating a protective layer that reduces friction and helps to cool down the engine.
Key Functions of 4-Stroke Engine Oil
- Lubrication: The most important job of 4-stroke oil is to lubricate the moving parts. This reduces wear and tear, helping your engine last longer.
- Cooling: As oil moves through the engine, it carries heat away from hot parts, helping to prevent overheating.
- Cleaning: Engine oil also picks up dirt, debris, and tiny metal particles, keeping the engine clean. These particles are then trapped in the oil filter.
- Protection Against Corrosion: Special additives in 4-stroke oils help to prevent rust and corrosion from forming inside the engine.
Expert Tip: Always check the oil level and quality regularly. Old or dirty oil can lead to engine problems like increased friction and heat, which may damage the engine over time.
What Makes 4-Stroke Oil Different?
A big difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine oils is that 4-stroke oils stay inside the engine. This means they need to be formulated differently to handle high temperatures and long periods of use. They are typically made with higher concentrations of additives, including:
- Detergents: Help clean the engine and prevent deposits from building up.
- Anti-wear agents: Protect critical engine parts from wearing out.
- Dispersants: Prevent dirt and sludge from sticking together, so they stay suspended in the oil.
- Antioxidants: Protect the oil itself from breaking down due to high heat.
Here’s a breakdown of the core differences between 2-stroke and 4-stroke oils:
| Feature | 2-Stroke Oil | 4-Stroke Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Mixed with fuel, burns during combustion | Circulates through the engine, not burned |
| Oil Change Interval | Added with fuel, doesn’t require an oil change | Requires regular oil changes |
| Additives | Fewer additives | More additives for lubrication and cleaning |
Personal Experience as an Expert Mechanic
In my 13 years as a mechanic, I’ve seen countless engines fail simply because the owner didn’t use the right oil or failed to change it at the correct intervals. One particular incident that stands out is a client who brought in a high-mileage Toyota that was running on the wrong oil for over a year. The oil had thickened, clogged the engine, and led to a costly repair. After that, I always remind customers to stick to what their owner’s manual recommends for oil types and change intervals.
How to Choose the Right 4-Stroke Engine Oil
When you’re choosing oil for a 4-stroke engine, there are a few key things to look for:
- Viscosity Rating: This is usually shown as something like 10W-30. It tells you how thick or thin the oil is at different temperatures.
- Tip: A lower first number (like 5W) is better for cold starts, while a higher second number (like 30) provides more protection in hotter conditions.
- Oil Type: You can choose between conventional, synthetic, or semi-synthetic oils.
- Conventional Oil: Good for basic engine protection, often cheaper.
- Synthetic Oil: Offers better protection under extreme conditions like high heat, making it ideal for high-performance vehicles.
- Semi-Synthetic Oil: A blend that offers some of the benefits of both at a lower price point.
Valvoline is one of the top brands in this space, offering excellent options for 4-stroke engines, especially their high-mileage oils and racing oils, which are designed to perform well under pressure.
Pro Tip: Always check the engine oil level using the dipstick and change your oil regularly, as recommended by the manufacturer. Fresh oil is critical for keeping your engine performing at its best.
When to Change Your 4-Stroke Engine Oil
For most cars, oil changes are needed every 3,000 to 5,000 miles. However, some newer cars and synthetic oils can go up to 7,500 or even 10,000 miles. Always consult your vehicle’s manual for exact recommendations. For motorcycles and other small engines, the interval might be shorter, so it’s always best to check.
In conclusion, 4-stroke engine oil is a critical component of engine health. It lubricates, cools, and cleans your engine, ensuring that it runs smoothly and efficiently. Choosing the right oil for your engine and maintaining it regularly will help you avoid expensive repairs and keep your vehicle in top shape for years to come.
By understanding these key points, you’ll ensure that your 4-stroke engine performs at its best, whether it’s in your car, motorcycle, or other vehicles.
Key Differences Between 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engine Oils
Understanding the differences between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine oils is critical for anyone looking to maintain the efficiency and longevity of their vehicle or machinery. These two engine types may look similar on the surface, but the oils they require are fundamentally different in composition and performance.
Let’s break down the key differences in a way that’s easy to follow.
1. Oil Mixing vs. Circulating
- 2-Stroke Oil: In a 2-stroke engine, the oil mixes with the fuel. That means the oil isn’t stored in the engine but instead combines with the fuel and burns during operation. Every time the engine runs, it consumes some of the oil along with the fuel.
- Think of it like cooking with oil—each time you cook, you need to add more oil.
- 4-Stroke Oil: On the other hand, 4-stroke engines use oil in a different way. Here, the oil circulates through the engine, lubricating the moving parts. It doesn’t burn with the fuel, so you don’t need to refill it with every tank of gas. Instead, it stays inside the engine and needs to be changed periodically.
- It’s like using oil in a car’s engine—it stays there for a while, doing its job, but eventually needs to be replaced.
2. Additive Composition
Another significant difference lies in the types of additives used in the oil. These additives are crucial for ensuring the oil can handle the demands of the engine.
- 2-Stroke Oil: This oil typically has fewer additives because it is designed to burn off with the fuel. You’ll find ingredients like:
- Detergents: To keep engine parts clean.
- Anti-wear agents: To reduce damage from friction.
- Fuel stabilizers: To help the fuel/oil mixture burn efficiently.
- 4-Stroke Oil: The oil in a 4-stroke engine is more complex. Since it circulates through the engine and isn’t burned off, it has a higher concentration of additives, including:
- Dispersants: To prevent sludge formation.
- Anti-wear additives: These are more essential in 4-stroke engines because the oil has to protect moving parts over a longer period.
- Foam retardants: To stop bubbles from forming when the oil is moving quickly through the engine.
3. Environmental Impact
When it comes to being environmentally friendly, the oils differ greatly.
- 2-Stroke Oil: Because the oil burns along with the fuel, it creates more emissions. Older 2-stroke engines are known for producing a smoky exhaust. This is why modern synthetic 2-stroke oils, like Valvoline SynPower 2T, are designed to minimize smoke and pollutants.
- 4-Stroke Oil: Since 4-stroke oil doesn’t burn, it produces fewer emissions. In fact, the oil helps engines run more efficiently, which can reduce the overall carbon footprint of the machine.
4. Performance and Maintenance
- 2-Stroke Oil: The performance of 2-stroke engines relies heavily on the quality of the oil. Since the oil burns off, it needs to provide protection in extreme conditions like high heat and fast-moving engine parts.
- Pro Tip from an Expert: Always use high-quality synthetic oil for small engines like chainsaws or dirt bikes. It’s a bit pricier, but it keeps the engine cleaner and running smoothly.
- 4-Stroke Oil: For 4-stroke engines, the oil’s primary job is to lubricate and cool the engine. The performance difference between a high-quality oil and a cheap one is noticeable, especially in high-performance applications like racing motorcycles.
- Expert Advice: Don’t just focus on price. Always check the oil’s viscosity rating (e.g., 5W-30). The right oil can make your engine run smoother and last longer.
5. Oil Change Frequency
- 2-Stroke Oil: Since it burns with the fuel, there’s no need to change the oil, but you do need to regularly refill the fuel/oil mix. Different machines will require different fuel-to-oil ratios, which range from 16:1 to 100:1. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- 4-Stroke Oil: For 4-stroke engines, you’ll need to change the oil periodically, just like you would in a car. How often depends on the engine, but most small engines require an oil change every 50 hours of use. For cars, it could be every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, depending on the oil and driving conditions.
Summary of Key Differences
Here’s a quick list to sum up what we’ve covered:
- 2-Stroke Oil:
- Mixes with fuel and burns off.
- Fewer additives.
- Requires frequent refills (fuel/oil mix).
- Produces more emissions.
- 4-Stroke Oil:
- Circulates within the engine.
- Contains more additives for protection.
- Requires periodic oil changes.
- Lower emissions and more efficient.
In conclusion, choosing the right oil for your engine is crucial. If you’re using a 2-stroke engine, focus on getting a high-quality synthetic oil that minimizes smoke and buildup. For 4-stroke engines, make sure you’re using an oil with the right additives to keep your engine running smoothly for years to come.
Why Choosing the Right Engine Oil Matters
Choosing the correct engine oil is more than just following a label on a bottle—it’s about ensuring your engine works smoothly, lasts longer, and performs at its best. Whether you’re driving a motorcycle, using a chainsaw, or maintaining a lawnmower, the oil you pick plays a critical role in how your engine functions. Let’s break this down.
Engine Performance and Longevity
When you use the right engine oil, it lubricates the moving parts of the engine, reducing friction. Friction is like the enemy of your engine. Without proper lubrication, parts will grind against each other, wear out faster, and even cause overheating. Imagine a bike chain without oil—it squeaks, it grinds, and eventually, it breaks down. The same thing happens to your engine if you’re not using the right oil.
- 2-Stroke Engines: These engines burn oil along with fuel, so the oil needs to mix well and burn cleanly. Using the wrong oil can lead to clogging, poor combustion, and even smoky exhaust.
- 4-Stroke Engines: The oil circulates through the engine instead of burning with the fuel, so it needs to be able to handle heat and stay thick enough to lubricate. Poor oil choices here can lead to poor lubrication and overheating.
Here’s a quick list of what the right oil ensures:
- Reduced friction between parts.
- Better temperature control by absorbing heat.
- Cleaner engine by preventing sludge buildup.
- Longer engine life by minimizing wear.
Fuel Efficiency
Using the right oil directly affects how efficiently your engine burns fuel. For example, in 2-stroke engines, if the oil doesn’t burn properly with the fuel, it can lead to incomplete combustion, which means your engine needs more fuel to do the same job. This translates to higher fuel consumption.
On the other hand, if your 4-stroke engine doesn’t get the right oil, it won’t run as smoothly. This means the engine has to work harder, using more fuel to keep things running. It’s like riding a bike with flat tires—it’s much harder to move forward!
- Tip from an Expert: I’ve personally seen people neglect oil quality in their small engines, like lawnmowers, only to wonder why their fuel bills are suddenly higher. It’s amazing how quickly fuel efficiency can drop when you’re not using the right oil.
Environmental Impact
Engines running on the wrong oil can produce more emissions. This is especially true for 2-stroke engines. When you burn the wrong type of oil, you’re not just affecting your engine but also the environment. Excessive smoke, more pollutants, and a lot of wasted fuel all contribute to environmental damage.
- For 2-stroke engines, modern synthetic oils help minimize emissions.
- For 4-stroke engines, using high-quality oil reduces unburned fuel emissions.
Valvoline, for instance, offers synthetic oil solutions designed specifically to minimize environmental impact by reducing smoke and emissions.
Personal Anecdote
In my 13 years of experience as an auto mechanic, I’ve seen countless engines come in for repair just because someone didn’t choose the right oil. I once had a customer bring in a go-cart with a completely gummed-up engine—turns out, they were using oil designed for a 4-stroke engine in their 2-stroke machine. The difference in oil types isn’t just marketing; it’s about how the oil interacts with the engine’s internal processes.
Expert Advice: Watch Out for Oil Quality
It’s not just about choosing the right type of oil (2-stroke vs. 4-stroke); quality matters too. Cheap oils may not have the same high-quality additives, like detergents or anti-wear agents, that premium oils offer. These additives are crucial for preventing sludge, keeping the engine clean, and making sure the oil performs well under extreme conditions.
Here’s a quick comparison of what high-quality oils offer compared to cheaper alternatives:
| Feature | High-Quality Oil | Low-Quality Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Additives | Rich in detergents, anti-wear | Fewer or lower-quality additives |
| Sludge prevention | Excellent at keeping engine clean | Sludge buildup is common |
| Heat resistance | Maintains viscosity at high temps | Breaks down under heat |
| Emissions | Lower emissions, cleaner burning | Higher emissions |
Choosing the right engine oil is essential for engine health, fuel efficiency, and environmental responsibility. Whether you’re using a 2-stroke or 4-stroke engine, picking the correct oil not only protects your engine but also ensures that it runs at peak performance. If you care about how well your machine operates—and how long it will last—make sure you’re using the right oil every time.
This simple but crucial decision can save you from bigger headaches down the road. If you’re unsure about which oil is best for your engine, consult your owner’s manual or ask a professional, like me!
2-Stroke vs. 4-Stroke Engine Oil: A Simple Guide to Choosing the Right One
When you have a machine powered by a small engine, knowing the difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines is essential. These engines might look similar, but their operation and oil needs are very different.
In this guide, we’ll dive deep into what makes 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines unique, how to choose the right oil for each, and why it matters.
What Are 2-Stroke Engines?
A 2-stroke engine is a type of engine that completes a full power cycle in just two movements of the piston: an upward stroke and a downward stroke.
Key Features:
- Simple Design: 2-stroke engines have fewer parts than 4-stroke engines.
- High Power: They fire every time the piston moves up, which gives them more power for their size.
- Common Uses: You’ll find 2-stroke engines in small machines like chainsaws, dirt bikes, and leaf blowers.
Expert Tip: “Because 2-stroke engines are more compact and lightweight, they are perfect for portable tools and smaller machines. However, they burn oil mixed with fuel, making them less environmentally friendly.”
Advantages:
- Lightweight and portable.
- High power output for their size.
Disadvantages:
- Less fuel-efficient.
- They create more pollution.
How 2-Stroke Engines Work
In a 2-stroke engine, every time the piston moves up or down, an event like combustion happens. This is why 2-strokes can generate more power quickly. However, they don’t have separate intake or exhaust valves, which leads to less fuel efficiency and more pollution.
What Are 4-Stroke Engines?
A 4-stroke engine requires four separate piston movements (intake, compression, power, and exhaust) to complete one power cycle. This makes them more efficient and cleaner than 2-stroke engines.
Key Features:
- More Efficient: 4-stroke engines use fuel more efficiently and burn less oil.
- Quieter and Smoother: These engines tend to run more quietly with less vibration.
- Common Uses: Found in cars, motorcycles, lawnmowers, and most modern vehicles.
Advantages:
- Better fuel efficiency.
- Lower emissions.
Disadvantages:
- More complex design.
- Heavier and larger than 2-stroke engines.
How 4-Stroke Engines Work
The engine takes four strokes of the piston to complete a cycle. First, the intake valve opens, letting in fuel and air. Then, the piston compresses the mixture, and the spark plug ignites it, providing power. Finally, the exhaust valve opens to release the gases.
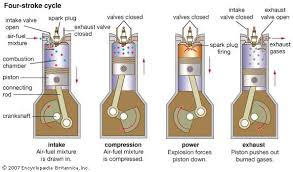
image source Britanica
What Is 2-Stroke Engine Oil?
In a 2-stroke engine, oil is mixed directly with fuel. This means that the oil is burned along with the fuel, which creates more emissions.
Types of 2-Stroke Oil:
- Synthetic Oil: Best for low emissions and high performance.
- Semi-Synthetic Oil: A blend of synthetic and petroleum oils.
- Petroleum-Based Oil: Older but still used in some machines.
Pro Advice: “When using 2-stroke oil, always follow the fuel-to-oil ratio recommended by the manufacturer. If you use too much oil, it can cause build-up, and too little can damage the engine.”
Popular 2-Stroke Oil Additives:
- Detergents: Help keep the engine clean.
- Anti-wear Agents: Protect moving parts from damage.
- Antioxidants: Prevent oil from breaking down too quickly.
What Is 4-Stroke Engine Oil?
Unlike 2-stroke oil, 4-stroke engine oil doesn’t mix with fuel. It circulates throughout the engine, keeping moving parts lubricated, cooling the engine, and cleaning away impurities.
Types of 4-Stroke Oil:
- Synthetic Oil: Excellent for high-performance engines like race cars.
- Conventional Oil: Used in most everyday passenger vehicles.
- High-Mileage Oil: Designed for vehicles with more than 75,000 miles.
Popular 4-Stroke Oil Additives:
- Dispersants: Keep impurities suspended in the oil, so they don’t stick to engine parts.
- Foam Retardants: Prevent the oil from foaming up, ensuring smooth operation.
How to Choose the Right 4-Stroke Oil
Always use the viscosity (thickness) recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer, like 5W-30 or 10W-40. The right oil helps the engine run smoothly, especially in extreme temperatures.
Key Differences Between 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engine Oil
- Mixing: 2-stroke oil mixes with fuel; 4-stroke oil stays separate.
- Burning: 2-stroke oil burns with fuel, while 4-stroke oil is recycled through the engine.
- Additives: 4-stroke oils generally have more additives to protect the engine over long periods.
| Feature | 2-Stroke Engine Oil | 4-Stroke Engine Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Burns with fuel | Does not burn, circulates in engine |
| Oil Type | Mixed with fuel | Separate from fuel |
| Common Use | Small tools, chainsaws, go-karts | Cars, motorcycles, lawnmowers |
| Additives | Simple additives | More complex, for long-term engine care |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions, less efficient | Lower emissions, more efficient |
Table Show Key Differences Between 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engine Oil
Why Choosing the Right Oil Matters
Choosing the right engine oil is more than just picking a brand. It’s about making sure your engine runs smoothly, efficiently, and for as long as possible.
Benefits of Using the Correct Oil:
- Better Performance: Using the correct oil helps your engine perform at its best.
- Longer Engine Life: Proper lubrication reduces wear and tear on engine components.
- Fuel Efficiency: The right oil can improve fuel efficiency, saving you money at the pump.
- Environmental Impact: Choosing cleaner oils, especially synthetics, helps reduce harmful emissions.
Expert Insight: “Always check your owner’s manual for the recommended oil. Using the wrong oil can lead to engine damage, poor performance, and costly repairs.”
Here’s a list of FAQs related to 2-stroke vs 4-stroke engine oil:
1. What is the difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine oil?
- Answer: The main difference is that 2-stroke oil mixes with fuel and burns, while 4-stroke oil circulates separately to lubricate engine parts without burning.
2. Can you use 4-stroke oil in a 2-stroke engine?
- Answer: No, 4-stroke oil cannot be used in a 2-stroke engine as it is not designed to burn with fuel, which could lead to engine damage.
3. Why does 2-stroke oil burn with the fuel?
- Answer: In 2-stroke engines, oil is mixed with fuel to lubricate moving parts since the engine design does not have a separate oil system like 4-stroke engines.
4. What is the fuel-to-oil ratio for 2-stroke engines?
- Answer: The ratio typically ranges from 16:1 to 100:1, depending on the engine type. Always refer to your equipment’s manual for the recommended ratio.
5. Which oil is more environmentally friendly—2-stroke or 4-stroke?
- Answer: 4-stroke engines are generally more environmentally friendly because they burn fuel more efficiently and produce fewer emissions compared to 2-stroke engines.
6. Can synthetic oil be used in both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines?
- Answer: Yes, synthetic oil can be used in both types of engines, but ensure you use the correct formulation (2-stroke or 4-stroke) for your engine.
7. Why is 4-stroke oil preferred for cars?
- Answer: 4-stroke oil is preferred for cars because it offers better lubrication, longer engine life, and lower emissions, making it more suitable for daily use in vehicles.
8. How often should I change the oil in a 4-stroke engine?
- Answer: For most 4-stroke engines, oil should be changed every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer.
9. Can 2-stroke engines use high-mileage oil?
- Answer: No, high-mileage oil is typically formulated for 4-stroke engines. 2-stroke engines require oil that is mixed with fuel for proper function.
10. What happens if I use the wrong engine oil?
- Answer: Using the wrong engine oil can lead to poor engine performance, excessive wear, and even potential engine damage over time. Always use the oil specified by your engine manufacturer.
11. How do I know if my engine is 2-stroke or 4-stroke?
- Answer: A quick way to tell is by checking the fuel system. 2-stroke engines require oil to be mixed with fuel, while 4-stroke engines have a separate oil reservoir. Additionally, 2-stroke engines are often found in smaller tools and machines, while 4-strokes are common in cars and larger equipment.
12. Can I switch between synthetic and conventional oil in a 4-stroke engine?
- Answer: Yes, you can switch between synthetic and conventional oil in a 4-stroke engine, but it’s recommended to do so during an oil change and consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure compatibility.
13. Why does 2-stroke oil smoke more than 4-stroke oil?
- Answer: 2-stroke oil tends to smoke more because it burns with the fuel, which can lead to visible exhaust smoke. 4-stroke oil, on the other hand, does not burn, which reduces smoke and emissions.
14. How can I reduce emissions from my 2-stroke engine?
- Answer: To reduce emissions, use high-quality synthetic 2-stroke oil, which burns cleaner, and make sure you are mixing the correct fuel-to-oil ratio. You can also regularly maintain the engine to ensure it runs efficiently.
15. What are the signs of poor oil quality in a 4-stroke engine?
- Answer: Signs of poor oil quality include thick or dirty oil, increased engine noise, overheating, sluggish performance, and the oil having a burnt smell. If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to change the oil.
16. Is 2-stroke oil more expensive than 4-stroke oil?
- Answer: Generally, 2-stroke oil can be more expensive on a per-use basis because it is burned along with fuel, so you use it more frequently. However, 4-stroke oil can be more expensive upfront due to higher concentrations of additives, especially synthetic varieties.
17. Can I use multi-grade oil in a 4-stroke engine?
- Answer: Yes, multi-grade oil, like 10W-30 or 5W-40, is commonly used in 4-stroke engines because it works effectively in a range of temperatures, providing better protection in cold starts and under high heat.
18. Why do 2-stroke engines tend to wear out faster than 4-stroke engines?
- Answer: 2-stroke engines wear out faster because they operate at higher RPMs and generate more heat with each cycle. The lack of a dedicated lubrication system also leads to more wear on engine components.
19. What is the lifespan of 2-stroke and 4-stroke oils?
- Answer: For 2-stroke oils, you mix it fresh with fuel for each use, so it doesn’t stay in the engine long-term. For 4-stroke engines, oil should typically be changed every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or based on the manufacturer’s recommendation.
20. Do 2-stroke and 4-stroke oils have different additives?
- Answer: Yes, 4-stroke oils generally have more complex additives like detergents, dispersants, anti-wear agents, and foam retardants, while 2-stroke oils focus more on minimizing ash content and reducing smoke emissions during combustion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine oils is key to maintaining your engine’s health. Whether you’re maintaining a chainsaw or driving your daily commuter car, using the right oil ensures better performance, a longer lifespan, and reduced environmental impact.
Key Takeaways:
- 2-stroke engines are simpler, lighter, and found in smaller machines, but they burn oil with fuel, creating more emissions.
- 4-stroke engines are more complex, fuel-efficient, and common in cars and motorcycles, using oil that circulates separately from the fuel.
Remember, always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil type and viscosity to keep your engine running smoothly.

Author: Frank Jenkins
Frank Jenkins – Family Car Expert and Safety Advocate
Frank Jenkins, steering you towards safer and smarter family driving. Based in: New York, New York, USA
About Me
Greetings from New York City! I’m Frank Jenkins, your navigator in the world of family vehicles and automotive safety. With over 15 years of experience as an automotive writer and safety consultant, I focus on what matters most to families on the go. Through rigorous testing and detailed research, I ensure that your next family car is not only comfortable and stylish but also packed with the latest safety features.
Contact Information
Topics of Interest
- Family-Friendly Car Reviews
- Vehicle Safety Systems
- Child Passenger Safety
- Road Trip Planning and Car Entertainment
Memberships
More About Frank
Short Bio: Frank Jenkins has become a household name for parents seeking advice on the best and safest cars for their families. His reviews are infused with a parent’s concern and an engineer’s precision. Education: Bachelor of Science in Automotive Technology from the New York University Qualifications: Certified Child Passenger Safety Technician (CPST) Languages: English (Native), French (Intermediate) Previous Roles:
- Safety Feature Columnist for Family Wheels Magazine
- Technical Advisor for Safe Car Campaigns
- Host of “The Safe Family Road Trip” Podcast
Fun Fact: Frank once organized a cross-country road safety workshop, visiting over 50 cities in 30 days.
Interactive Features
- Safety First with Frank: A forum dedicated to discussing and sharing best practices for family road safety.
- Frank’s Philosophy: “The best family memories are made in cars that put safety above everything else.”
- Your Stories: A section for readers to share their family road trip experiences and car-related anecdotes.
Featured Content
Newest Articles:
- “The Ultimate Guide to Family Cars in 2024”
- “Innovations in Car Safety: What Families Need to Know”
Highlighted Content:
- “Minivan or SUV: The Great Family Debate Resolved”
- “Child Seats 101: Choosing the Right One for Your Car”
Recommended Reads:
- “The Road to Safety: How Cars Have Become Safer for Children”
- “Entertaining Your Kids on the Road: Tips and Tricks”
Multimedia Spotlight:
- Podcast: “Drive Time Family” – Discussions on making family travel safer and more enjoyable
- Video Series: “Car Seat Clinics” – Demonstrations on proper car seat installation and usage
Editorial Team & Collaborations
Frequent Co-authors:
- Emily Chen, Urban Driving Specialist
- Marcus O’Reilly, Off-Road Adventure Guru
Editorial Staff Overview: A team of dedicated writers and safety experts committed to helping families make informed decisions about their vehicles. Editorial Guidelines: We are steadfast in providing transparent and practical advice that prioritizes the well-being of all passengers.
Journey With Me
For reliable reviews, safety advice, and the best in family automotive, hit the road with Frank Jenkins at oilforcar.com