Choosing the right engine oil for your vehicle isn’t just a technical choice. It’s essential for ensuring optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and long-term reliability. One critical factor to consider is whether the oil meets ACEA specifications. ACEA stands for the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association, which sets standards to help choose the right engine oil for your vehicle.
What is ACEA?
ACEA stands for Association des Constructeurs Européens d’Automobiles—or, in English, the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association.
Founded in 1991, this organization plays a significant role in Europe’s automotive industry. It sets standards not just for vehicles but also for engine lubricants, ensuring oils meet the requirements of modern engines. The founding members included some of the biggest names in the auto world, such as BMW, Volkswagen, Renault, and Volvo. Today, ACEA also represents non-European manufacturers with operations in Europe.
Why Was ACEA Created?
When you think about the diversity of engines—petrol, diesel, hybrid—it’s clear that one-size-fits-all oil doesn’t work. ACEA was established to:
- Define oil performance standards to meet varying engine needs.
- Support sustainability goals by ensuring oils improve engine efficiency and reduce harmful emissions.
- Adapt oil requirements to keep pace with emerging technologies, such as turbochargers and advanced after-treatment systems.
By doing this, ACEA helps keep engines running smoothly and supports environmental regulations.
How ACEA Standards Work
The heart of ACEA’s work lies in its Oil Sequences. These sequences are updated regularly to ensure they align with new engine designs, emission laws, and technological advancements.
Here’s a timeline showing some key updates:
| Year | Major Update |
|---|---|
| 1996 | First ACEA Oil Sequences introduced (replacing CCMC). |
| 2010 | New emission regulations prompted changes in oil specifications. |
| 2022 | Latest sequences for heavy-duty engines released. |
Key Point: ACEA does not certify oils. Instead, manufacturers create oils that meet these standards, which are later tested independently.
ACEA Oil Categories Explained
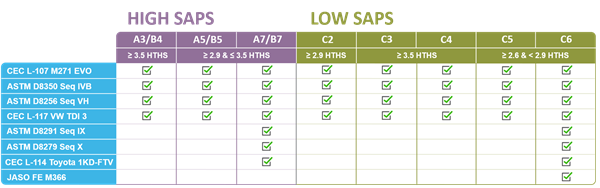
ACEA oils are divided into three major categories. Each has a letter (indicating the class) and a number (showing its specific sub-category).
1. ACEA A/B: Petrol and Light-Duty Diesel Engines
These oils are designed for high-performance engines. They maintain stability under demanding conditions, such as long-distance driving or heavy loads.
Sub-categories include:
- A1/B1: Low-friction, low-viscosity oils that improve fuel efficiency.
- A3/B3: Durable oils for extended drain intervals in harsh conditions.
- A7/B7: Advanced oils protecting against wear in turbocharged engines.
2. ACEA C: Low-SAPS and Mid-SAPS Oils
The C category focuses on oils compatible with modern exhaust systems, such as Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs).
- Low-SAPS oils have reduced levels of harmful substances like phosphorus and sulfur, which can damage emission systems.
- Mid-SAPS oils balance performance and environmental requirements.
| C Sub-Category | SAPS Level | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | Low | Sensitive systems with strict emission controls. |
| C3 | Mid | High-performance petrol and diesel engines. |
| C6 | Mid | Turbocharged engines needing low-speed pre-ignition protection. |
3. ACEA E: Heavy-Duty Diesel Engines
These oils are designed for commercial vehicles and industrial applications. They provide superior protection under extreme conditions.
Examples include:
- E4: For long drain intervals in Euro 4 and 5 engines.
- E11: Latest standard for diesel engines with DPFs.
Why ACEA Standards Matter
ACEA specifications ensure:
- Engine Longevity: Oils meeting ACEA standards protect against wear, deposits, and corrosion.
- Environmental Compliance: These oils reduce emissions by improving combustion efficiency.
- Warranty Coverage: Using the wrong oil may void your car’s warranty.
A Personal Take: An Expert’s Advice
As someone who has worked with engines for over a decade, I can tell you that choosing the right oil isn’t just about price or availability. I’ve seen engines fail prematurely because drivers ignored ACEA recommendations.
For example, a customer once used a non-ACEA-approved oil in a DPF-equipped car. Within months, the DPF clogged, leading to costly repairs. This could have been avoided by simply checking the owner’s manual and choosing an ACEA-compliant oil.
Tip: Always consult your vehicle’s manual. If unsure, ask a professional.
Interactive Data: Viscosity and ACEA Class
Here’s an example of how ACEA classifications correlate with viscosity standards:
| ACEA Class | Viscosity | Engine Type |
|---|---|---|
| A3/B4 | 5W-30 | Petrol & Direct Injection Diesel |
| C3 | 0W-30 | High-Performance Diesel |
| E6 | 15W-40 | Heavy-Duty Diesel |
What are ACEA Oil Sequences?
The ACEA Oil Sequences are a set of engine oil standards developed by the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA). These standards ensure engine oils meet specific performance and environmental requirements. Over time, they have become essential for maintaining modern engines’ health and efficiency.
Why Are ACEA Oil Sequences Important?
Modern engines are more advanced and efficient than ever. They need oils that protect against wear, improve fuel efficiency, and work well with advanced emissions systems. The ACEA standards help ensure oils meet these needs by setting clear guidelines for:
- Lubrication quality
- Emission system compatibility
- Engine durability
Regular Updates to ACEA Oil Sequences
ACEA oil sequences are not static. They evolve to match new technologies, environmental regulations, and engine designs. Since the first release in 1996, updates have been issued regularly, often in response to stricter emissions rules or technological advancements. For instance:
- 2021 Update: Focused on improving oil performance for engines using biofuels.
- 2022 Update: Adjusted for heavy-duty engines to meet stricter emission and durability requirements.
Key Features of ACEA Oil Sequences
- Defined by Performance: Oils must pass stringent tests for wear protection, cleanliness, and oxidation stability.
- Compatibility with Emissions Systems: Modern engines often use Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) or Three-Way Catalysts (TWCs). ACEA sequences ensure oils won’t harm these components.
- Environmental Considerations: The standards help reduce emissions by encouraging the use of low-ash and low-phosphorus oils.
Categories of ACEA Oil Sequences
ACEA oil sequences are divided into three main classes, each tailored to specific engine types:
1. ACEA A/B: Petrol and Light-Duty Diesel Engines
- Designed for high-performance petrol engines and light-duty diesel engines.
- Includes subcategories like:
- A1/B1: Low-friction oils that enhance fuel efficiency.
- A3/B3: High-performance oils for engines under severe conditions.
2. ACEA C: Catalyst-Compatible Oils
- Oils in this category are compatible with advanced emissions systems.
- Subcategories include:
- C1 and C4: Low-SAPS (low sulphated ash, phosphorus, and sulphur) oils for sensitive engines.
- C3 and C5: Mid-SAPS oils balancing performance and emissions system protection.
3. ACEA E: Heavy-Duty Diesel Engines
- Developed for heavy-duty applications like trucks and buses.
- Examples:
- E7: Suitable for engines operating in severe conditions.
- E11: Advanced oils supporting newer emissions technologies like SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction).
How to Identify the Right ACEA Oil for Your Engine
Every oil label includes the ACEA classification, like C3 or E9. To choose the correct oil, follow these steps:
- Check Your Vehicle Manual: Manufacturers often specify the required ACEA class.
- Match the Oil Type: Ensure the ACEA grade matches your engine type and driving conditions.
- Avoid Mismatched Oils: Using the wrong ACEA oil can harm your engine or void its warranty.
Expert Insights
As an auto expert with years of experience, I’ve seen engines fail due to incorrect oil use. Once, a customer used a non-ACEA-approved oil in their diesel car with a DPF. Within months, the filter was clogged, leading to costly repairs. Always ensure your oil meets ACEA standards for peace of mind.
FAQs About ACEA Oil Sequences
- Do ACEA oil sequences apply globally?
They are widely used in Europe but recognised worldwide due to their strict quality standards. - Can I mix ACEA oils?
No. Mixing oils can reduce performance and may damage the engine. - What happens if I use the wrong ACEA oil?
It could lead to engine wear, higher emissions, or even a voided warranty.
ACEA oil sequences are a vital guide for selecting the right oil for your engine. They ensure engines stay efficient, emissions systems remain protected, and performance stays high. By understanding these standards, you can make informed decisions to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Understanding European Oil Standards: ACEA Specifications
Ensuring the longevity of your vehicle’s engine requires the right oil. One crucial factor is adhering to the standards defined by ACEA—the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association. These specifications are critical for selecting the correct oil, offering compatibility with your engine and environmental regulations.
Fun Fact:
ACEA replaced older CCMC standards in 1996 to introduce more robust classifications for oils.
Why ACEA Specifications Matter
ACEA-approved oils ensure:
- Engine Protection: Oils reduce wear and deposits while maintaining performance.
- Environmental Compliance: Compatibility with filters and catalytic converters lowers emissions.
- Warranty Safety: Using ACEA-compliant oils protects your warranty.
ACEA Oil Classifications
The ACEA framework divides oils into three main categories based on engine type and performance requirements.
1. A/B Class
For petrol (A) and light-duty diesel (B) engines.
- A1/B1: Low-friction oils for better fuel economy.
- A3/B3: High-performance oils, suitable for longer intervals.
- A3/B4: Designed for direct-injection diesel engines.
- A5/B5: Balances fuel efficiency and high shear strength.
- A7/B7: Protects turbocharged engines and reduces pre-ignition risks.
2. C Class (Catalyst-Compatible Oils)
C oils cater to engines with sensitive emission systems like Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs).
- C1: Low-SAPS oils for maximum protection of after-treatment devices.
- C2/C3: Mid-SAPS oils for versatile performance.
- C4: Stable oils suitable for modern Euro 6 engines.
- C5/C6: Advanced mid-SAPS oils optimised for fuel efficiency.
Tip for Vehicle Owners:
Always check your manual to confirm whether your car needs low-SAPS or mid-SAPS oil.
3. E Class (Heavy-Duty Oils)
For larger diesel engines in commercial vehicles.
- E4/E6: Designed for extended drain intervals in Euro 5 and Euro 6 engines.
- E9/E11: Protect particulate filters while maintaining high performance.
Glossary of Key Terms
Here are simple explanations for terms you might encounter:
Total Base Number (TBN)
A measure of how much acid the oil can neutralise. High TBN means the oil offers better corrosion protection.
HT/HS (High-Temperature/High-Shear)
This measures an oil’s ability to maintain viscosity under heat and pressure. Oils with higher HT/HS provide better wear protection.
SAPS
Short for Sulfated Ash, Phosphorus, and Sulphur. Lower SAPS content protects sensitive emission systems like DPFs.
Selecting the Right Oil for Your Engine
Follow these steps to ensure you pick an ACEA-approved oil:
- Check Your Owner’s Manual: Look for the ACEA grade recommended for your vehicle.
- Consider Emission Systems: Vehicles with DPFs often require low-SAPS oils.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult an expert mechanic or oil distributor.
Why It’s Crucial to Choose Correctly
Using the wrong oil can:
- Damage engine components.
- Poison catalytic converters and filters.
- Void your car’s warranty.
Expert Insight: When ACEA Saved the Day
As an auto mechanic, I once encountered a vehicle suffering from clogged filters. The culprit? The owner had used oil without checking the ACEA classification. Switching to a compatible C2 oil restored performance in no time.
SAPS Content Across ACEA Grades
SAPS Levels in ACEA Oils
| Grade | SAPS Level | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | Low | DPFs and sensitive systems |
| C3 | Mid | Balanced performance |
| E6 | Low | Heavy-duty vehicles |
ACEA Oil Classifications
Understanding ACEA oil classifications is essential for anyone maintaining or servicing a car. These classifications ensure the oil you use is suitable for your vehicle’s engine, enhancing performance and longevity. Let’s break it down into manageable pieces so that even a beginner can grasp it.
What Are ACEA Oil Classifications?
ACEA, or the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association, categorises oils based on their performance and purpose. This helps car owners and mechanics select the correct oil type for their vehicles.
ACEA divides engine oils into three main groups:
- A/B: For petrol (A) and light-duty diesel (B) engines.
- C: For engines requiring oils compatible with after-treatment devices like Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs).
- E: For heavy-duty diesel engines in commercial vehicles.
Why Do ACEA Classifications Matter?
Using the wrong oil can harm your engine. ACEA classifications help avoid this by ensuring the oil meets specific standards. These standards relate to engine protection, emissions control, and compatibility with modern technologies.
Key Features of ACEA Oils
- High-Temperature/High-Shear (HT/HS): Determines how oil behaves under extreme heat and stress.
- SAPS Levels: Refers to Sulfated Ash, Phosphorus, and Sulphur content, which can affect exhaust systems.
- Total Base Number (TBN): Indicates oil’s ability to neutralise acids formed during combustion.
The Three Groups of ACEA Oils
1. ACEA A/B Oils
This group is for petrol and light-duty diesel engines. These oils are versatile and offer stability across various driving conditions. They are further divided into:
- A1/B1: Low-friction, low-viscosity oils designed to improve fuel efficiency.
- A3/B3: Ideal for engines requiring high performance and long service intervals.
- A3/B4: Suitable for direct-injection diesel engines.
- A5/B5: A high-performance, low-viscosity option for newer engines.
- A7/B7: Advanced oils offering enhanced protection for modern turbocharged engines.
2. ACEA C Oils
Designed for cars with after-treatment systems like DPFs or three-way catalysts (TWCs). These oils have reduced SAPS content to avoid clogging filters.
- C1: Low-SAPS oils with minimal ash content.
- C2: Mid-SAPS oils for improved wear protection.
- C3: Similar to C2 but with higher viscosity for better high-stress protection.
- C4: Stable, low-SAPS oils designed for specific engine types.
- C5 & C6: Advanced mid-SAPS oils offering greater efficiency and protection in modern engines.
3. ACEA E Oils
This group is tailored for heavy-duty diesel engines used in trucks and commercial vehicles. These oils are built to withstand severe operating conditions and prolonged use.
- E4: For high-performance engines with extended drain intervals.
- E6: Compatible with emission-reduction systems like SCR.
- E7: Suitable for older and newer engines under heavy loads.
- E9: Balances performance and protection for engines with DPFs.
- E11: A recent improvement on E9, offering better protection against wear and tear.
Expert Insights
Why Should You Care About SAPS?
In my experience as a mechanic, oils with high SAPS content are excellent for older engines. However, modern engines with after-treatment systems require low-SAPS oils. Ignoring this can cause expensive damage, especially to DPFs, which cost a lot to replace.
My Tip for ACEA Oils
Always check your car’s manual. Manufacturers like Volkswagen or BMW specify which ACEA oils suit their engines. Never substitute one grade for another without confirmation. A customer once brought a turbocharged engine ruined by using an incompatible oil. It taught me how critical these classifications are.
Comparing ACEA Oils
Here’s a simple table to help you understand the differences:
| Classification | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| A/B | Petrol & light-duty diesel | Stability across temperatures |
| C | After-treatment systems | Reduced SAPS content |
| E | Heavy-duty commercial engines | Long intervals and high performance |
Understanding ACEA Oil Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide
What Are ACEA Oil Specifications?
The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) sets oil standards to ensure compatibility and performance across various engine types. These specifications guide oil manufacturers in creating lubricants suitable for modern engines, promoting optimal performance and protection.
This article explains ACEA oil categories, what they mean for your vehicle, and how choosing the right oil can make a difference.
The Importance of ACEA Standards
ACEA standards ensure oils are:
- Compatible with advanced engines.
- Designed to meet strict emission regulations.
- Tested for wear, fuel efficiency, and overall durability.
Each update to the ACEA sequences reflects advancements in engine technology and regulatory demands.
Detailed Breakdown of ACEA Oil Categories
ACEA specifications use letters and numbers to classify engine oils. Here’s what they mean:
1. ACEA A/B Oils: Petrol and Light-Duty Diesel Engines
These oils are for everyday cars and offer stability and long-lasting performance. The categories include:
- A1/B1: Low-friction oils that improve fuel economy but may not suit all engines.
- A3/B3: Designed for high-performance engines and long drain intervals.
- A3/B4: Compatible with advanced direct-injection diesel engines.
- A5/B5: High-tech, low-viscosity oils for reduced engine wear.
- A7/B7: Suitable for turbocharged engines needing superior anti-wear and deposit protection.
2. ACEA C Oils: Catalyst-Compatible Oils
These oils have reduced levels of sulphated ash, phosphorus, and sulphur (SAPS). This makes them ideal for modern emission systems like Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs). Categories include:
- C1: Low-SAPS, offering high fuel economy and robust protection.
- C2: Mid-SAPS, balancing protection and fuel efficiency.
- C3: Mid-SAPS oils that offer stronger wear protection than C2 oils.
- C4: Similar to C1 but with higher heat stability.
- C5: Focused on reducing CO₂ emissions with low HT/HS viscosity.
- C6: Provides advanced protection against low-speed pre-ignition in turbocharged engines.
3. ACEA E Oils: Heavy-Duty Diesel Engines
These oils are specifically designed for trucks and commercial vehicles:
- E4: High-performing oils for Euro 3 to Euro 5 engines with extended drain intervals.
- E6: Suitable for engines meeting Euro 4, 5, and 6 standards, offering excellent emissions control.
- E7: Oils for demanding heavy-duty applications in Euro 3 to 5 engines.
- E9: Designed for advanced emission control and durability in Euro 4, 5, and 6 engines.
- E11: The latest, most efficient mid-SAPS heavy-duty oil standard.
Key Terms to Know
Before diving deeper, here are some essential terms:
- TBN (Total Base Number): Measures the oil’s ability to neutralise acids. Higher TBN is better for engines using high-sulphur fuels.
- HT/HS Viscosity: Indicates the oil’s stability under high temperature and shear conditions.
- SAPS: Refers to Sulphated Ash, Phosphorus, and Sulphur. Lower levels protect sensitive emission systems.
HTML Table of ACEA Categories
| Category | Application | Features |
|---|---|---|
| A/B | Petrol and light-duty diesel engines | Low-friction, high-performance options |
| C | Engines with DPF and TWC systems | Low-SAPS and mid-SAPS oils |
| E | Heavy-duty diesel engines | High durability and emission compliance |
Choosing the Right ACEA Oil
Each vehicle manufacturer provides guidelines for oil compatibility. For example:
- Volkswagen specifies oils like VW 502 00 for petrol engines and VW 509 00 for modern diesel engines.
- Using non-compliant oils can harm the engine and void your warranty.
Tips for Choosing Oil:
- Check your vehicle manual for ACEA specifications.
- Verify compatibility with your car’s emission systems.
- Use oils with the latest ACEA standards for better performance.
Personal Anecdote from an Expert
As a mechanic, I’ve seen engines damaged due to the wrong oil type. One customer had a modern turbo diesel but used an older non-SAPS oil. It clogged the DPF, leading to expensive repairs. This highlights the importance of following ACEA guidelines.
Wrapping Up
ACEA oil specifications are crucial for engine health. They ensure:
- Proper lubrication.
- Reduced emissions.
- Long-lasting engine performance.
By selecting the right ACEA-approved oil, you protect your vehicle and ensure it runs efficiently for years. Always consult your manual or an expert if unsure.
Choosing the Right Engine Oil
Selecting the correct engine oil for your vehicle is crucial. It ensures your engine runs smoothly, efficiently, and lasts longer. But how do you know which oil is right? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
Why Engine Oil Matters
Engine oil does more than just lubricate. It protects against wear, cools the engine, and keeps it clean by reducing sludge. Using the wrong oil can cause severe damage, affecting engine performance and lifespan.
Understanding Oil Types
Engine oils are not one-size-fits-all. Each type is formulated for specific engine designs and operating conditions. Here are the main types you should know:
- Mineral Oils
- Made from refined crude oil.
- Best for older engines or those with simpler requirements.
- Synthetic Oils
- Created through chemical engineering.
- Offer superior performance in high and low temperatures.
- Semi-Synthetic Oils
- A blend of mineral and synthetic oils.
- Provide better protection than mineral oils at a lower cost than full synthetics.
- High-Mileage Oils
- Designed for engines with over 75,000 miles.
- Contain additives that protect aging components.
Reading the Labels
When choosing oil, you’ll notice numbers like 5W-30 on the bottle. These numbers refer to the oil’s viscosity or thickness.
- The first number (e.g., 5W) shows how the oil flows in cold temperatures.
- The second number (e.g., 30) shows its performance at operating temperature.
Pro Tip: Check your vehicle’s manual for the recommended viscosity range. Using the wrong viscosity can lead to poor lubrication or overheating.
What Are ACEA Standards?
European vehicles often follow ACEA (European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association) standards. These ensure the oil meets specific requirements for wear, emissions, and engine cleanliness. For instance:
- A/B Series oils are suitable for petrol and light-duty diesel engines.
- C Series oils are for modern engines with diesel particulate filters (DPFs).
Consider Your Driving Habits
Your driving style and environment can also influence your oil choice:
- Short trips in cold weather? Choose oils with low-temperature protection, like 0W-20.
- Long-distance or towing? Opt for oils with high shear strength, like 5W-40.
- Urban stop-and-go traffic? Synthetic oils may reduce engine stress.
Manufacturer Recommendations Are Key
Always follow your car manufacturer’s guidelines. Using oils outside their specifications can void warranties and harm your engine. For instance, BMW recommends Longlife-04 oils, while Volkswagen uses its own VW 504 00/507 00 standards.
Expert Advice: Keep It Simple
From my 13 years in the automotive industry, I’ve seen engines fail due to poor oil choices. A customer once brought in a car running on low-grade oil that wasn’t ACEA-certified. The engine suffered from clogged components and overheating. A simple switch to the manufacturer-recommended oil could have prevented this costly repair.
How to Choose the Right Oil
Here’s a step-by-step checklist:
- Check the owner’s manual. Look for the recommended viscosity and standards (e.g., API, ACEA).
- Understand your car’s needs. Is it petrol, diesel, or a hybrid? Does it have DPF or catalytic converters?
- Consider the climate. For colder regions, go for oils with better low-temperature flow.
- Review your driving habits. Regular commutes and heavy loads need oils with stronger wear resistance.
- Look for certifications. Ensure the oil is approved by ACEA or API.
Quick Reference Table
| Oil Type | Best For | Example Viscosity |
|---|---|---|
| Mineral | Older engines | 10W-40 |
| Synthetic | Extreme temperatures | 5W-30, 0W-20 |
| Semi-Synthetic | Balanced performance | 10W-30 |
| High-Mileage | Over 75,000 miles | 5W-30 High Mileage |
Keep It Fresh
Changing your oil regularly is just as important as using the right type. Follow the manufacturer’s suggested intervals, and always use a quality oil filter. Neglecting oil changes can lead to sludge buildup and engine damage.
Why ACEA Standards Matter for Vehicle Owners and Manufacturers
When it comes to choosing engine oil, you might have come across ACEA specifications. But why do they matter? Let’s explore the significance of these standards and how they impact both vehicle owners and manufacturers.
What are ACEA Standards?
The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) sets oil standards to ensure consistent quality and performance. These specifications cater to the unique requirements of various engines, from small petrol engines to heavy-duty diesel systems.
Unlike some global standards, ACEA specifications evolve regularly. They incorporate new technologies and stricter emission regulations. This makes them highly relevant in today’s automotive landscape.
A Quick Glossary of Key Terms
Before diving deeper, here are a few important terms:
- TBN (Total Base Number): Measures the oil’s ability to neutralise acids.
- HT/HS (High Temperature/High Shear): Refers to oil performance under extreme heat and stress.
- SAPS (Sulfated Ash, Phosphorus, and Sulphur): A measure of substances that can affect emissions systems like Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs).
The Impact on Vehicle Owners
1. Ensuring Proper Engine Performance
ACEA-approved oils are designed to:
- Minimise wear and tear.
- Enhance engine longevity.
- Improve fuel efficiency.
Using oils without ACEA approval may lead to poor engine health or reduced performance.
2. Protecting After-Treatment Systems
Modern vehicles rely on after-treatment systems like DPFs or three-way catalytic converters. Low-SAPS oils, for instance, protect these sensitive parts from clogging or damage.
3. Preventing Warranty Issues
Manufacturers often mandate specific oil standards. If non-approved oil is used, your warranty could be voided. For example, Volkswagen specifies oils meeting their own ACEA-based standards like VW 504 00 or VW 509 00.
The Manufacturer’s Perspective
1. Uniform Quality Control
ACEA standards ensure manufacturers work with oils that meet stringent criteria. This simplifies global production while ensuring reliability across vehicles.
2. Adapting to Emissions Regulations
The automotive industry must meet tough European emissions laws. ACEA sequences align with these requirements, helping manufacturers achieve compliance.
For example:
- C-grade oils cater to vehicles equipped with DPFs or catalytic converters.
- E-grade oils support heavy-duty engines that meet Euro 6 standards.
Why Regular Updates are Critical
ACEA standards aren’t static. They are updated to reflect:
- Advances in fuel-efficient engine designs.
- Stricter environmental rules.
- Improvements in lubrication technologies.
The latest update, ACEA 2022, added new classifications like C6 oils, which protect against turbocharger deposits in modern engines.
Expert Tips for Vehicle Owners
Choosing the Right Oil
- Check your owner’s manual for ACEA recommendations.
- Understand your car’s emission system needs (e.g., DPF or catalytic converter).
- Use tools like Valvoline’s Lubricant Advisor to match oils to your engine.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Don’t mix oils with different ACEA specifications. It may reduce their effectiveness.
- Avoid over-extending oil change intervals. Even ACEA-approved oils degrade over time.
ACEA Oil Standards Timeline
| Year | Update | Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1996 | Initial ACEA Sequences | Replaced CCMC standards |
| 2010 | Low-SAPS Grades | Aligned with Euro 5 emissions |
| 2022 | New Heavy-Duty Classifications | Stricter fuel economy targets |
Conclusion
ACEA standards are essential for maintaining your vehicle’s engine health. They guide manufacturers and car owners in selecting the best oils for modern engines.
Always follow these steps:
- Check your vehicle’s manual for ACEA requirements.
- Choose oil that matches both ACEA and OEM guidelines.
- Replace oil regularly to ensure optimal performance.
By following these simple tips, you’ll protect your engine, improve fuel efficiency, and extend your vehicle’s lifespan.
Author: Jordan Miles
Jordan Miles – Senior Automotive Editor
Jordan Miles, a journey through the world of automotive marvels. Based in: Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA
About Me
Hello, I’m Jordan Miles! I’ve been in love with the roar of engines and the sleek lines of automotive design since I could remember. With over a decade of experience in automotive journalism, I bring you the latest insights, deep dives into car technology, and spotlight the most exciting trends in the world of automobiles. From the heart of the USA, join me on a journey to discover the cars that set our pulses racing and the future models that promise to revolutionize our roads.
Contact Information
Email: jordan@oilforcar.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/jordan_mil13743/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/miles.jordan.89
Topics of Interest
Electric and Hybrid Innovation
American Muscle Cars
Classic Car Restoration
Future Automotive Technologies
Memberships
Automotive Press Association (APA)
Electric Vehicle Association (EVA)
More About Jordan
Short Bio: A renowned automotive expert and a fixture at auto shows across the country, Jordan brings a blend of technical knowledge and a passion for storytelling. Education: B.S. in Mechanical Engineering, with a focus on Automotive Design from MIT. Qualifications: Certified Automotive Reviewer by the National Auto Critics Association (NACA). Languages: English (Native), Spanish (Fluent) Previous Roles:
Test Driver for Performance Car Magazine
Consultant for Car Restoration TV Shows
Engineer Intern at Tesla Motors
Fun Fact: Once restored a 1967 Shelby GT500 with nothing but a workshop manual and a lot of determination.
Interactive Features
Ask Jordan: Have a burning question about your favorite car? Drop me a line, and let’s talk torque and horsepower.
Jordan’s Quotes: “The perfect car is a fusion of art, technology, and the freedom of the open road.”
Reader’s Corner: Share your thoughts on the latest reviews and join the discussion!
Featured Content
Newest Articles:
The Resurgence of the American Muscle Car
Electric Dreams: How EVs are Charging into the Mainstream
Highlighted Content:
Behind the Wheel: An In-depth Review of the 2024 Mustang
The Evolution of Safety Features in Modern Cars
Recommended Reads:
A Week with the Tesla Roadster: The Future is Now
Under the Hood: The Mechanics of Autonomous Vehicles
Multimedia Spotlight:
Podcast: “Revving Up” – Weekly discussions on car culture and new models
Video Series: “Garage Tours” – A sneak peek into America’s most fascinating car collections
Editorial Team & Collaborations
Frequent Co-authors:
Alex Rivera, our Electric Vehicle Expert
Maria Chen, Classic Car Enthusiast and Columnist
Editorial Staff Overview: A dedicated team bringing you the most accurate and engaging car reviews and news. Editorial Guidelines: Commitment to unbiased reporting and in-depth analysis of automotive models.
Stay Connected
For the latest car reviews, industry insights, and a look at automotive history through the lens of today, keep your engines revving with Jordan Miles at oilforcar.com.