Synthetic oil is a lubricant made from chemically modified materials rather than crude oil, which is typically used to produce conventional motor oil. This oil is engineered to provide superior performance, especially in extreme conditions. The development of synthetic oils stems from the need for lubricants that can handle high temperatures, heavy loads, and the stresses of modern engines more effectively than traditional oils.
Synthetic oil is crafted through a complex chemical process that involves the breakdown of crude oil into its basic molecules, then reassembled with customized properties. This allows manufacturers to tailor the oil’s performance characteristics to suit specific needs. Here are some notable features of synthetic oil:
- Enhanced Stability: Synthetic oils maintain their viscosity and performance at extreme temperatures, making them ideal for high-performance and turbocharged engines.
- Reduced Impurities: Unlike conventional oils, synthetic oils have fewer impurities and undesirable compounds, resulting in better engine protection and longevity.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: The chemical structure of synthetic oil can reduce friction more effectively than traditional oil, contributing to better fuel economy.
There are different types of synthetic oils, such as full synthetic and synthetic blends. Full synthetic oil is entirely lab-engineered, while synthetic blends combine synthetic oil with conventional oil to offer some benefits at a lower cost. With advances in automotive technology, synthetic oil has become a popular choice among vehicle owners seeking better performance, engine protection, and longevity.
Understanding the Types of Synthetic Oil
Synthetic oil is a man-made lubricant created from chemical compounds that are engineered to provide better performance and protection for engines. Unlike conventional oil, which is refined from crude oil, synthetic oil is tailored molecule by molecule to meet specific needs, making it more effective under various driving conditions.
There are two main types of synthetic oils: Full Synthetic Oil and Synthetic Blend Oil. Each of these has its unique characteristics and benefits. Understanding the differences between these types of synthetic oils can help consumers make informed decisions when choosing the right oil for their vehicles.
Full Synthetic Oil
Full synthetic oils are composed entirely of synthetic base oils, which are engineered to have uniform molecular structures. This uniformity allows full synthetic oil to provide superior protection and performance across a wide range of temperatures and conditions. The benefits of full synthetic oil include:
- Better engine protection: Full synthetic oils are specifically designed to reduce friction, which minimizes engine wear and extends the engine’s life.
- Enhanced performance in extreme temperatures: Synthetic oil flows better in cold temperatures, reducing the risk of engine wear during start-up, and it remains stable at high temperatures, protecting the engine under heavy loads.
- Longer oil change intervals: Due to its high resistance to degradation, full synthetic oil lasts longer than conventional oil, allowing for extended oil change intervals (often between 5,000 to 15,000 miles depending on the brand and vehicle).
For instance, Mobil 1 full synthetic oil is known for its “superior performance in high-performance engines,” which makes it ideal for drivers who expect top-tier protection and longevity from their oil.
Synthetic Blend Oil
Synthetic blend oils combine conventional mineral oil with synthetic base oils. This type of oil provides a balance between affordability and enhanced protection compared to standard mineral oils. Although it doesn’t offer the same high level of performance as full synthetic oil, it still offers improved protection over conventional oil. Some benefits of synthetic blend oil include:
- Cost-effective option: Blends are more affordable than full synthetic oils while still offering better protection and performance than conventional oils.
- Improved protection in higher temperatures: Synthetic blends resist breakdown better than conventional oils, providing extra protection in demanding driving conditions, such as towing or hauling heavy loads.
- Enhanced oxidation resistance: Compared to conventional oils, synthetic blends have a higher resistance to oxidation and chemical degradation, which helps maintain engine cleanliness over time.
While synthetic blends are a good compromise for budget-conscious drivers, they may not last as long or provide as much protection as full synthetic oils, especially in extreme conditions.
Special Types of Synthetic Oils
In addition to full synthetic and synthetic blends, there are specialized types of synthetic oils designed for particular uses:
- High-mileage synthetic oils: These are formulated for engines with over 75,000 miles, containing additives that help condition seals and reduce oil consumption.
- PAO-based synthetic oils: These are made from polyalphaolefins (PAOs), offering high thermal stability and low volatility, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles and extreme driving conditions.
As synthetic oils continue to evolve, the types of base stocks used can vary, affecting the oil’s properties. “PAOs, for instance, offer excellent viscosity control and oxidation resistance, making them a popular choice for synthetic formulations used in automotive engines.”
By understanding the types of synthetic oils available, you can make more informed choices based on your driving habits, vehicle requirements, and budget. Whether you opt for full synthetic oil for maximum protection or a synthetic blend for a more cost-effective solution, the key is to ensure that the oil meets the needs of your vehicle and driving conditions.
Synthetic Oil vs. Conventional Oil
The debate between synthetic and conventional oil is ongoing, with each offering distinct benefits and drawbacks depending on a vehicle’s needs and driving conditions. Synthetic oil is artificially made, created through a complex chemical process that restructures petroleum molecules for enhanced performance. In contrast, conventional oil is derived from refined crude oil, making it a more natural, though less refined, option.
Synthetic oil, due to its engineered properties, provides certain performance advantages over conventional oil. One key benefit is its ability to withstand extreme temperatures better. Synthetic oils are formulated to retain optimal viscosity across a wider range of conditions, meaning they remain fluid in cold weather and resist thinning when engines run hot. Conventional oils, on the other hand, tend to thicken in cold weather and degrade more quickly at high temperatures.
Key Differences
- Oxidation Resistance: Synthetic oils have superior resistance to oxidation, meaning they degrade slower when exposed to engine heat and contaminants, which leads to less sludge formation. Conventional oils are more prone to breaking down, leading to increased sludge and deposits over time.
- Temperature Performance: “Synthetic oils flow better at low temperatures,” which ensures better engine protection during cold starts, a time when wear is most likely to occur. Conversely, conventional oils may become too thick, delaying circulation and protection.
- Longevity: Synthetic oil generally lasts longer between oil changes, with some formulations allowing for 5,000 to 7,000 miles, or even up to 25,000 miles in certain cases. Conventional oil, by comparison, often needs changing every 3,000 to 5,000 miles.
Despite these benefits, synthetic oil has its drawbacks. The most notable is its higher price, which can be two to four times more expensive than conventional oil. This cost difference can add up, especially for routine maintenance over the vehicle’s lifetime. However, with synthetic oil’s longer change intervals, the additional cost may be offset by less frequent servicing.
Here is a comparison table of synthetic oil vs. conventional oil based on the key differences discussed:
| Aspect | Synthetic Oil | Conventional Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Base Composition | Artificially made through chemical processing | Refined from natural crude oil |
| Oxidation Resistance | High resistance to oxidation, less sludge buildup | Prone to oxidation, leading to more sludge |
| Temperature Performance | Maintains viscosity in both hot and cold extremes | Thicker in cold, thins out faster in heat |
| Engine Start Protection | Flows better during cold starts, providing faster protection | Slower to circulate, risking more engine wear |
| Longevity/Change Interval | Longer intervals (5,000-25,000 miles) | Shorter intervals (3,000-5,000 miles) |
| Cost | Higher price (2-4 times more expensive) | Lower cost |
| Engine Cleanliness | Cleaner, less likely to form deposits | More likely to form deposits and sludge over time |
| Environmental Impact | Generally produces fewer emissions | Can contribute more to environmental pollution |
| Fuel Efficiency | May slightly improve fuel economy due to better lubrication | Standard performance |
| Vehicle Suitability | Best for high-performance engines or extreme driving conditions | Suitable for regular, older, or less-demanding engines |
| Manufacturer Recommendation | Follow manufacturer’s advice; sometimes required | Often recommended for older or basic vehicles |
In summary, while synthetic oils offer superior performance in many areas such as longevity, temperature stability, and sludge resistance, the decision to use synthetic or conventional oil should ultimately depend on the specific needs of your vehicle and your driving habits. “Always follow the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations” regarding oil types and change intervals, as using a higher grade of oil may not always provide significant benefits in everyday driving conditions.
Advantages of Synthetic Oil
Synthetic oil offers a variety of advantages over conventional motor oil, making it a popular choice for many car owners. One of its most significant benefits is its “resistance to chemical degradation.” Due to its molecular structure and advanced refining process, synthetic oil withstands the breakdown caused by heat, oxidation, and contaminants better than conventional oil. This resistance helps protect engine components and keeps the oil functioning longer, meaning fewer oil changes and lower long-term maintenance costs.
Another notable advantage of synthetic oil is its ability to perform well under extreme temperatures. In cold climates, synthetic oil remains fluid and circulates through the engine more quickly than conventional oil, reducing wear during cold starts. In hot environments, it resists thinning, which helps maintain engine lubrication at high operating temperatures. This thermal stability is crucial for protecting engines exposed to heavy loads or harsh driving conditions.
The “longer oil change intervals” offered by synthetic oil is another compelling benefit. While conventional oil typically needs to be changed every 3,000 to 5,000 miles, synthetic oils can last between 7,500 and 15,000 miles, depending on the vehicle and driving conditions. This not only reduces the time and cost associated with oil changes but also contributes to less environmental waste.
Key advantages include:
- Oxidation and degradation resistance: Synthetic oil lasts longer and protects engines better.
- Thermal stability: It performs well in both extremely hot and cold temperatures.
- Longer oil change intervals: Fewer oil changes result in cost savings and less waste.
- Improved engine cleanliness: Synthetic oils contain fewer impurities, which helps reduce sludge and deposit buildup in the engine, keeping it cleaner over time.
The combination of synthetic oil’s resistance to breakdown, stability in extreme temperatures, and extended service life makes it a superior choice for long-term engine performance and protection.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Oil
While synthetic oil offers many advantages over conventional oil, it also has several notable disadvantages that should be considered before making a switch. Here are some key drawbacks:
- Higher Cost
One of the most significant disadvantages of synthetic oil is its cost. Synthetic oil is substantially more expensive than conventional oil, with prices ranging from two to four times higher. This cost difference can be a deciding factor for many car owners. “Five quarts of full synthetic oil will set you back about $45, while an oil change with full synthetic oil costs about $70,” making it a more costly option for regular maintenance.
- Synthetic oil can cost up to four times more than conventional oil
- Oil changes with synthetic oil are significantly more expensive
- Additive Precipitation
Another potential drawback is that synthetic oil may experience additive precipitation under certain conditions, particularly in cold temperatures. This means that some of the additives, which are essential for improving performance, can separate from the oil during storage or when exposed to low temperatures. This issue can reduce the effectiveness of the oil and lead to engine problems if not addressed properly.
- Additives may separate from the oil during cold storage
- Separation can affect oil performance and engine protection
- Lower Fuel Economy
Though synthetic oils generally perform better, they can slightly reduce fuel economy under certain conditions. Some studies suggest that synthetic multi-grade oils may provide less fuel efficiency at highway speeds compared to conventional oils. This is due to the unique way synthetic oils interact with certain engine components, which can result in a marginal decrease in fuel mileage.
- Potential for reduced fuel economy, especially during highway driving
- The difference may not be significant, but it can still be a factor for some drivers
- Compatibility Issues
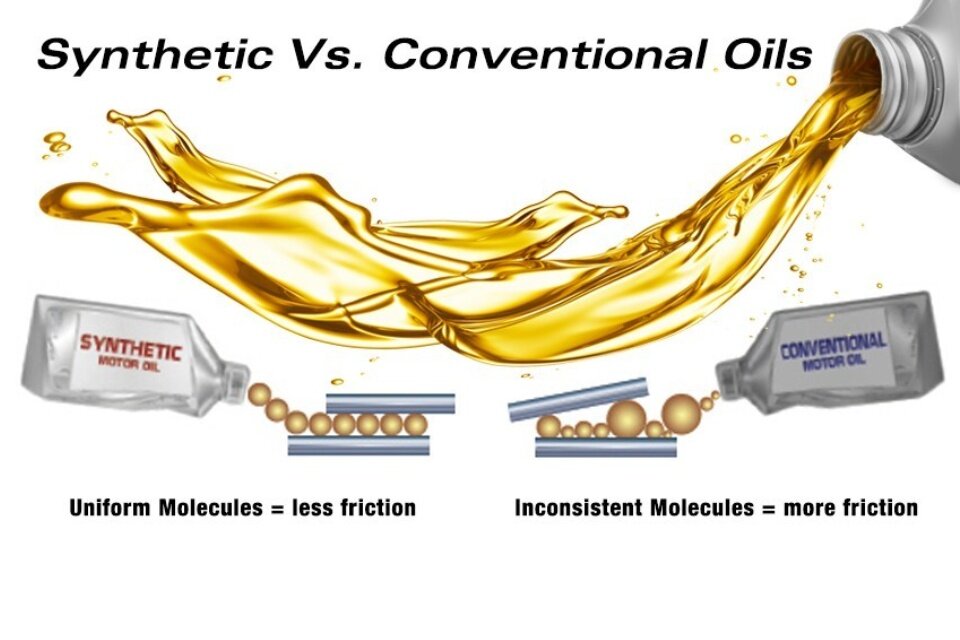
Synthetic oil can sometimes cause leakage in older engines or engines not designed for its use. The smaller, more uniform molecules of synthetic oil may slip through seals and gaskets that are slightly worn, leading to leaks. Additionally, certain synthetic oils are not always compatible with older engines, making it important to verify compatibility before switching.
- May cause leaks in older or high-mileage engines
- Not always compatible with older engine models or seals
- Potential for Overuse
Lastly, the extended life of synthetic oils can lead to overuse. Since synthetic oils offer longer intervals between oil changes (up to 7,000 miles or more), some drivers may delay changing their oil beyond the recommended period. Even though synthetic oil lasts longer, it’s still important to follow manufacturer guidelines for oil change intervals. Prolonging oil changes can lead to sludge buildup or other engine issues.
- Extended oil life can result in delayed oil changes
- Risk of sludge or deposits forming if oil is not changed regularly
Though these disadvantages may not outweigh the benefits for everyone, it’s essential to consider them when deciding whether synthetic oil is the right choice for your vehicle.
Here’s a comparison table that highlights the advantages and disadvantages of synthetic oil:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | – Superior engine protection | – May experience additive precipitation in cold temps |
| – Better viscosity at extreme temperatures | ||
| Longevity | – Longer oil change intervals (up to 7,000 miles or more) | – Can lead to overuse and delayed oil changes |
| Fuel Efficiency | – Potentially improved fuel economy | – Slightly reduced fuel economy in some cases |
| Engine Cleanliness | – Reduces engine deposits and sludge buildup | – May cause leaks in older or high-mileage engines |
| Temperature Stability | – Performs well in both high and low temperatures | – Not always compatible with older engine models |
| Cost | – Generally offers better value over time | – Higher initial cost compared to conventional oil |
When Should You Switch to Synthetic Oil?
Deciding when to switch to synthetic oil can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance and longevity. While conventional oil has served many engines well over the years, synthetic oils offer advantages that make them increasingly popular among car owners. Here are some considerations to help you determine the right time for the switch:
- Manufacturer Recommendations:
- Many modern vehicles are designed to run on synthetic oil. Check your owner’s manual. If it specifies synthetic or offers it as an option, you might consider making the switch, especially if you want to maximize performance and engine protection.
- Driving Conditions:
- If you frequently drive in extreme temperatures—either very hot or very cold—synthetic oil can provide better protection. It maintains viscosity better under high heat and remains fluid in low temperatures, ensuring optimal lubrication regardless of external conditions.
- Additionally, if your driving habits involve stop-and-go traffic, towing heavy loads, or extended highway driving, synthetic oil is beneficial. Its superior chemical stability helps reduce wear and tear in challenging conditions.
- Engine Age and Mileage:
- Consider switching if your vehicle has high mileage (typically over 75,000 miles) and has not used synthetic oil before. While synthetic oil can provide excellent cleaning properties, high-mileage engines may have accumulated deposits that need addressing. It is advisable to ease into the transition by opting for shorter oil change intervals initially to allow the synthetic oil to clean the engine effectively.
- If your engine is relatively new and you plan to keep it for a long time, transitioning to synthetic oil can enhance its performance and longevity.
- Performance Expectations:
- If you own a high-performance vehicle or participate in motorsports, synthetic oil is often essential. The demands placed on such engines can lead to rapid oil breakdown, and synthetic oils are engineered to handle these extremes.
- “In general, yes – provided the automaker’s viscosity grade and other oil requirements are adhered to,” advises Michael Calkins, Technical Services Manager for AAA. This indicates that high-performance and luxury vehicles can benefit significantly from synthetic lubricants.
- Budget Considerations:
- Although synthetic oil is generally more expensive than conventional oil—often costing two to four times as much—consider the longer oil change intervals it allows. The cost of synthetic oil may be offset by the reduced frequency of oil changes, making it a more economical choice in the long run. For instance, while conventional oil changes are recommended every 3,000 to 5,000 miles, synthetic oil can last between 5,000 and 15,000 miles, depending on the brand.
Switching to synthetic oil is a decision that should consider multiple factors, including manufacturer specifications, driving conditions, engine age, and performance needs. In many cases, the benefits of synthetic oil—such as enhanced protection, improved performance under extreme conditions, and longer change intervals—far outweigh the initial cost difference. By assessing your vehicle’s requirements and your driving habits, you can make an informed decision that best serves your engine’s needs.
Synthetic Oil Cost Comparison
When considering the transition from conventional to synthetic oil, one cannot overlook the significant differences in cost between the two. While synthetic oils are often praised for their superior performance and longevity, they do come with a higher price tag. Understanding this cost comparison is essential for consumers who are weighing the benefits against their budget.
Price Overview
On average, the cost of synthetic oil is two to four times higher than that of conventional oil. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Conventional Oil: A typical quart costs around $4 to $10, and an oil change with conventional oil averages about $38.
- Synthetic Oil: A quart generally ranges from $8 to $12 or more, with a full synthetic oil change costing about $70.
This discrepancy translates to an additional expenditure of approximately $64 per year for the average driver if they switch to synthetic oil. However, it’s important to note that the benefits gained from using synthetic oil might offset this initial increase in cost over time.
Long-Term Benefits
While the upfront cost is a significant factor, the long-term advantages of synthetic oil should be considered. Here are some potential savings and benefits:
- Extended Oil Change Intervals: Synthetic oils typically allow for longer intervals between changes, usually recommended every 5,000 to 7,000 miles, and in some cases, up to 25,000 miles depending on the brand.
- Reduced Frequency of Oil Changes: Due to the longer intervals, switching to synthetic oil could mean fewer visits to the mechanic, leading to savings on both oil and labor costs over the lifespan of the vehicle.
- Enhanced Engine Protection: With better thermal stability and resistance to oxidation, synthetic oils can help prolong engine life. This may result in fewer repairs and maintenance costs in the long run.
Cost vs. Value
In summary, while synthetic oils come with a higher price tag, their benefits often justify the expense. The longevity, enhanced performance, and protection they offer can lead to reduced overall vehicle maintenance costs. According to industry experts, “Investing in premium lubrication may slightly extend the life of your engine,” which ultimately may save you money on significant repairs down the line.
In conclusion, when evaluating whether to switch to synthetic oil, it’s crucial to assess both the immediate financial impact and the long-term benefits. Balancing these factors will enable you to make an informed decision that aligns with your vehicle’s needs and your budget.
Here’s a table summarizing the cost comparison between synthetic and conventional oil, along with their respective benefits:
| Aspect | Conventional Oil | Synthetic Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Average Cost per Quart | $4 to $10 | $8 to $12 or more |
| Average Oil Change Cost | Approximately $38 | Approximately $70 |
| Annual Additional Cost | N/A | ~$64 more than conventional oil |
| Recommended Oil Change Interval | Every 3,000 to 5,000 miles | Every 5,000 to 7,000 miles (up to 25,000 miles for some brands) |
| Frequency of Oil Changes | More frequent | Less frequent |
| Engine Protection | Basic protection | Enhanced thermal stability and oxidation resistance |
| Overall Long-Term Savings | Lower upfront cost | Potentially lower maintenance costs due to fewer repairs and extended engine life |
| Value Assessment | Good for short-term use | Better for long-term investment |
Summary of Benefits
- Conventional Oil: Lower initial costs, but more frequent changes needed.
- Synthetic Oil: Higher upfront costs, but longer intervals and better engine protection, potentially leading to savings on maintenance over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Synthetic Oil
Synthetic oil has become a popular choice among vehicle owners due to its numerous advantages over conventional oils. However, many questions often arise regarding its benefits, differences from conventional oil, and its suitability for various engines. Below are some of the most frequently asked questions about synthetic oil.
1. Is synthetic oil better than conventional oil?
Yes, synthetic oil generally offers superior performance compared to conventional oil. While conventional oils can provide adequate lubrication, they lack the enhanced properties that synthetics deliver. Synthetic oils are formulated with higher-quality base oils, resulting in:
- Greater chemical stability
- Improved resistance to oxidation and acid formation
- Enhanced protective qualities over time
In essence, synthetic oil helps to maintain engine health and performance far better than traditional options.
2. What are the advantages of synthetic oil over conventional oil?
Synthetic oils are engineered to deliver performance that conventional oils cannot match. Here are some key advantages:
- Improved Engine Protection: Synthetic oils offer better protection against wear, reducing the risk of engine damage.
- Cleaner Engines: They resist sludge and deposit formation, keeping engine components clean and efficient.
- Better Low-Temperature Flow: Synthetic oils can flow better in extremely cold conditions, ensuring immediate lubrication during startup.
- High-Temperature Stability: They maintain their integrity and performance under high temperatures, protecting engines from overheating.
These advantages stem from the advanced formulation of synthetic oils, which are designed to meet the demands of modern engines.
3. Does synthetic oil have longer oil change intervals than conventional oil?
Yes, synthetic oil typically allows for longer oil change intervals. Many synthetic oils can support intervals ranging from 7,500 miles to 20,000 miles, depending on the specific brand and product. This longer lifespan is due to the oil’s superior resistance to degradation and oxidation compared to conventional oils, which generally require changes every 3,000 to 5,000 miles.
However, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for your specific vehicle to ensure optimal performance.
4. What is the difference between full synthetic oil and synthetic blend oil?
While both types of oils contain synthetic components, they differ in their formulation. Full synthetic oils are composed entirely of synthetic base oils and are engineered for maximum performance. In contrast, synthetic blend oils typically combine conventional oil with synthetic base stocks. As a result, full synthetics provide enhanced protection and performance compared to blends, but blends still offer some benefits over conventional oils.
- Full Synthetic Oil:
- Higher quality base oil
- Superior performance and protection
- Synthetic Blend Oil:
- Combination of conventional and synthetic oils
- Cost-effective option with better performance than conventional oil
5. Can I switch from conventional oil to synthetic oil?
Absolutely! Switching from conventional to synthetic oil is not only possible but also beneficial for most vehicles. Synthetic oils are compatible with conventional oils, meaning that an engine flush is typically not required. However, if you own a high-mileage vehicle that has never used synthetic oil, it is advisable to transition gradually.
Start with more frequent oil changes to allow the synthetic oil to clean up any existing sludge or deposits effectively. After a few changes, you can begin to follow the recommended intervals for synthetic oils.
6. Is synthetic oil worth the extra cost?
While synthetic oil does come with a higher price tag—typically two to four times more than conventional oil—it often proves to be a wise investment. The longer oil change intervals and superior protection can lead to:
- Cost savings over time due to less frequent changes
- Increased engine longevity, reducing repair costs
- Improved fuel efficiency, potentially saving money at the pump
Considering these factors, the benefits of using synthetic oil may outweigh the initial expense, particularly for those planning to keep their vehicles for an extended period.
7. Can synthetic oil cause leaks in older engines?
One concern among owners of older vehicles is that switching to synthetic oil may cause leaks. While synthetic oils can clean up existing sludge and deposits, this characteristic can sometimes lead to the exposure of worn seals and gaskets that may have been previously coated with sludge. If the seals are old or already compromised, synthetic oil might exacerbate existing leaks.
However, it’s essential to note that:
- Not all older engines will experience leaks: Many older engines can benefit from synthetic oil without issues.
- Seal conditioners: Some synthetic oils contain additives designed to help swell and condition seals, potentially mitigating leakage.
If you’re considering the switch, it’s advisable to check your vehicle for any signs of wear before making the change.
8. Does synthetic oil perform well in extreme temperatures?
Yes, one of the standout features of synthetic oil is its ability to perform exceptionally well in extreme temperatures.
- Cold Weather: Synthetic oil flows better at low temperatures, which means it can circulate quickly during cold starts. This characteristic reduces engine wear when starting in frigid conditions.
- Hot Weather: In high-temperature conditions, synthetic oil resists breakdown and maintains its viscosity better than conventional oils. This resilience protects engine components from overheating and helps ensure consistent performance.
Overall, the thermal stability of synthetic oil makes it an excellent choice for vehicles operating in diverse climates.
9. What are the environmental benefits of using synthetic oil?
Using synthetic oil can also offer environmental advantages. Here are a few notable points:
- Reduced Oil Consumption: Longer oil change intervals mean less frequent disposal of used oil, leading to less environmental waste.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Synthetic oils can enhance fuel economy by reducing engine friction, leading to lower emissions and reduced fuel consumption.
- Recyclability: Many synthetic oils are recyclable, contributing to a more sustainable approach to vehicle maintenance.
By opting for synthetic oil, you may not only protect your engine but also contribute positively to the environment.
10. Are there any disadvantages to synthetic oil?
While synthetic oil has many advantages, there are a few potential downsides to consider:
- Cost: As mentioned earlier, synthetic oil typically costs more than conventional oil, which can be a significant factor for budget-conscious consumers.
- Compatibility: Although most modern engines can use synthetic oil without issues, some older engines may not be designed for it, necessitating caution before switching.
- Potential for Overkill: For some drivers, particularly those who do minimal driving and under gentle conditions, the benefits of synthetic oil may not justify the additional expense.
Ultimately, whether or not to use synthetic oil will depend on individual driving habits, vehicle type, and personal preferences.
Conclusion
In summary, synthetic oil stands out as a superior option for many vehicle owners due to its advanced formulation and enhanced performance characteristics. From better engine protection and longer oil change intervals to improved fuel efficiency and environmental benefits, synthetic oil presents numerous advantages. While there are considerations to keep in mind, such as potential leaks in older engines and higher costs, the overall benefits often outweigh these concerns.
As always, it is essential to consult your vehicle’s owner manual and consider your driving conditions when making decisions about oil types. Understanding the nuances of synthetic oil can lead to a more informed choice, ultimately enhancing both engine longevity and performance.
Author: Frank Jenkins
Frank Jenkins – Family Car Expert and Safety Advocate
Frank Jenkins, steering you towards safer and smarter family driving. Based in: New York, New York, USA
About Me
Greetings from New York City! I’m Frank Jenkins, your navigator in the world of family vehicles and automotive safety. With over 15 years of experience as an automotive writer and safety consultant, I focus on what matters most to families on the go. Through rigorous testing and detailed research, I ensure that your next family car is not only comfortable and stylish but also packed with the latest safety features.
Contact Information
Topics of Interest
- Family-Friendly Car Reviews
- Vehicle Safety Systems
- Child Passenger Safety
- Road Trip Planning and Car Entertainment
Memberships
More About Frank
Short Bio: Frank Jenkins has become a household name for parents seeking advice on the best and safest cars for their families. His reviews are infused with a parent’s concern and an engineer’s precision. Education: Bachelor of Science in Automotive Technology from the New York University Qualifications: Certified Child Passenger Safety Technician (CPST) Languages: English (Native), French (Intermediate) Previous Roles:
- Safety Feature Columnist for Family Wheels Magazine
- Technical Advisor for Safe Car Campaigns
- Host of “The Safe Family Road Trip” Podcast
Fun Fact: Frank once organized a cross-country road safety workshop, visiting over 50 cities in 30 days.
Interactive Features
- Safety First with Frank: A forum dedicated to discussing and sharing best practices for family road safety.
- Frank’s Philosophy: “The best family memories are made in cars that put safety above everything else.”
- Your Stories: A section for readers to share their family road trip experiences and car-related anecdotes.
Featured Content
Newest Articles:
- “The Ultimate Guide to Family Cars in 2024”
- “Innovations in Car Safety: What Families Need to Know”
Highlighted Content:
- “Minivan or SUV: The Great Family Debate Resolved”
- “Child Seats 101: Choosing the Right One for Your Car”
Recommended Reads:
- “The Road to Safety: How Cars Have Become Safer for Children”
- “Entertaining Your Kids on the Road: Tips and Tricks”
Multimedia Spotlight:
- Podcast: “Drive Time Family” – Discussions on making family travel safer and more enjoyable
- Video Series: “Car Seat Clinics” – Demonstrations on proper car seat installation and usage
Editorial Team & Collaborations
Frequent Co-authors:
- Emily Chen, Urban Driving Specialist
- Marcus O’Reilly, Off-Road Adventure Guru
Editorial Staff Overview: A team of dedicated writers and safety experts committed to helping families make informed decisions about their vehicles. Editorial Guidelines: We are steadfast in providing transparent and practical advice that prioritizes the well-being of all passengers.
Journey With Me
For reliable reviews, safety advice, and the best in family automotive, hit the road with Frank Jenkins at oilforcar.com

Pingback: Engine Oil Compatibility with Various Fuel Types - Explore Oil For Car -Motor Oil Maintenance and Car Tips
Pingback: The Impact of Low Viscosity Engine Oils on Engine Wear and Performance - Explore Oil For Car -Motor Oil Maintenance and Car Tips
Pingback: How Cold Temperatures Affect Engine Oil: Essential Tips for Winter Driving - Oil for Car – Car Oil Reviews, Guides, & Car Tips
Pingback: How to Extend the Life of Your Turbocharger: 7 Essential Maintenance Tips - Oil for Car – Car Oil Reviews, Guides, & Car Tips